Example 1 (solving for the hypotenuse)
| Use the Pythagorean theorem to determine the length of X | 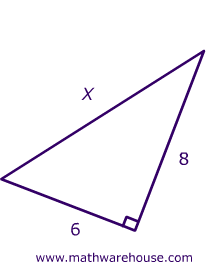 |
| Step 1) Identify the legs and the hypotenuse of the right triangle. | The legs have length '6 and '8' . 'X' is thehypotenuse because it is opposite the right angle. See Picture |
| Step 2) Substitute values into the formula (remember 'c' is the hypotenuse) | A2 + B2 = C2 62 + 82 = X2 |
| Step 3) Solve for the unknown |  |
Example 2 (solving for a Leg)
| Use the Pythagorean theorem to determine the length of X | 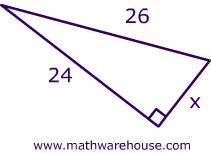 |
| Step 1) Identify the legs and the hypotenuse of the right triangle. | The legs have length '24' and 'X' are the legs. The hypotenuse is 26. See Picture |
| Step 2) Substitute values into the formula (remember 'c' is the hypotenuse) | A2 + B2 = C2 x2 + 242 = 262 |
| Step 3) Solve for the unknown |  |
Problem 1)
| Find the length of X |  |
| Step 1 |
Problem 2)
| Use the Pythagorean theorem to calculate the value of X.Round your answer to the nearest tenth. |  |
| Step 1 |
Problem 3)
| Use the Pythagorean theorem to calculate the value of X.Round your answer to the nearest hundredth.. | 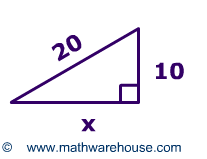 |
| Step 1 |
No comments:
Post a Comment